Freight Forwarder Insights
Huin International Logistics Latest Articles
Bill of Entry
What is Bill of Entry?
A bill of entry is a legal document that is filed by importers or customs clearance agents on or before the arrival of imported goods. It’s submitted to the Customs department as a part of the customs clearance procedure. Once this is done, the importer will be able to claim ITC on the goods. The bill of entry can be issued for either home consumption or bond clearance. When it is issued for bond clearance, the bond number and date of issuance should be included.
For the purpose giving information, goods are classified into three categories,
• Free Goods: These goods are not subjected to any customs duty.
• Goods for Home Consumption: These goods are imported for self-consumption.
• Bonded Goods: Where goods are subject to customs duty, till duty is paid, goods are kept in Bond.
Who should issue a bill of entry?
Bill of entry should be issued by:
• Firms that import goods from other countries.
• Firms that purchase goods from SEZ and sell them within India.
Procedure
Once the bill of entry is filed, an authorized Customs officer will examine the goods. Then the importer of goods should pay the basic customs duty, IGST, and GST compensation CESS to clear the goods. The importer can claim ITC for the IGST and compensation CESS, but not for the basic customs duty.
Format of a bill of entry:
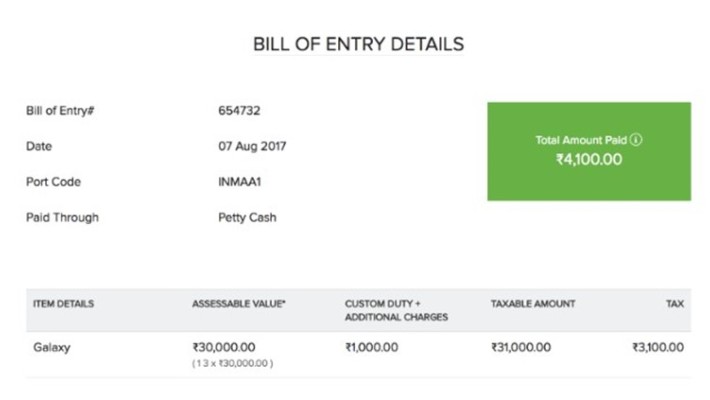
Based on the rules prescribed by the Government, here is what a sample bill of entry will look like in the GST regime. See the Port show in Figure 1.1.
• Port code and license number.
• Customs house agent code, Import Export code (IEC), and importer’s name and address. The address will be auto-populated if the importer is a registered taxpayer.
NOTE: Most taxpayers will enter their GSTIN (or provisional GSTIN) in the IEC field. If they don’t have a regular or provisional GSTIN, they can use their PAN/UIN. Based on this, the importer will be provided ITC for the IGST and compensation CESS that was paid to clear the goods. However, ITC cannot be claimed on the basic customs duty that is paid for the goods.
• Vessel’s name, port of shipment, country of origin and country code, country of consignment and its code (if different from the country of origin), date on which bill of lading was issued.
• Details regarding the goods and their value:
Packages and quantity
• Serial number, description of the goods, and unit code of the goods
• Number of packages and their weight or volume
• Description of the goods (details should be given separately for each class)
• Customs tariff heading, including the exemption notification and year
Customs duty
• Nature of the duty code
• Assessable value of the goods. Additional charges like landing and handling charges (if any) can be mentioned here.
• Basic rate and basic amount of customs duty levied
Additional duty
• Central Excise Tariff (CET) with respect to the exemption notification and year
• Special Additional Duty (SAD) for Customs
• Value, rate and total additional duty
IGST
• GST code, IGST rate, and IGST amount
• Compensation CESS amount
• Exemption notification for claiming exemption from IGST
• Exemption notification for claiming exemption from GST compensation CESS
• Total amount of duty (assessable value plus custom duty and additional charges) in words, and total number of packages in words
Two declaration and signature sections: One for the Customs house agent, and one for the importer.
Contents of Bill of Entry
• Name and address of importer.
• Name and address of exporter.
• Import license number.
• Name of port where goods are to be cleared.
• Description of goods.
• Value of goods.
• Rate and value of import duty payable.
Amendment of Bill of Entry
Whenever mistakes are noticed after submission of documents, amendments to the bill of entry is carried out with the approval of Deputy/Assistant Commissioner.
Prior Entry for Bill of Entry
For faster clearance of the goods, provision has been made in section 46 of the Act, to allow filing of bill of entry prior to arrival of goods. This bill of entry is valid if vessel/aircraft carrying the goods arrive within 30 days from the date of presentation of bill of entry.
The importer is to file 5 copies of the bill of entry and the fifth copy is called Advance Noting copy. The importer has to declare that the vessel/aircraft is due within 30 days and they have to present the bill of entry for final noting as soon as the IGM is filed. Advance noting is available to all imports except for into bond bill of entry and also during the special period.
Difference between bill of lading and bill of entry
Bill of Lading is document prepared by Liner Party (Shipping Line) for the purpose of the Shipment of the items. It shows the Consigner and Consignee and their Address, Port of
Loading and Unloading, Item Name, Quantity, Weight, CBM, Freight Details (sometimes) and Details of Container No and seal and Voyage in Vessel. By the Bill of Lading Number we can Track the container or our Shipment.
But The Bill of Entry is a document prepared by the customs Department showing the items are billed or imported and its classification are done for the purpose of Duty assessment. The bill of entry prepared on the basis of Bill of Lading, Commercial Invoice, Packing List, IEC code, IGM, Vat registration Certificate, and Pan Card etc... The bill of Entry is prepared by on the basis of importer or CHA declaration regarding the shipped or importing goods.