Freight Forwarder Insights
Huin International Logistics Latest Articles
Comprehensive Guide to Calculating Air Freight Costs: Steps and Example
When requesting airfreight services from a shipping company, you will typically be quoted an all-inclusive air freight rate. This comprehensive rate covers various charges such as the fuel surcharge, security inspection fee, airport operation fee, documentation fee, and customs fee.
Allow me to delve deeper into the subject of air freight. We will explore the nuances of air freight calculation, understanding how to determine the chargeable weight, identifying the factors that influence air freight costs, and strategies for minimizing these costs.
Air Freight Calculation
The cost structure for air freight primarily consists of two components: the base air freight rate and various surcharges.
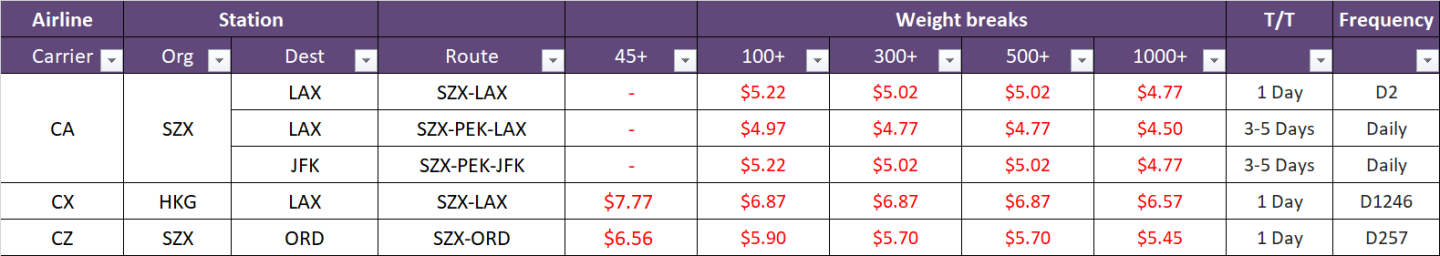
Typically, the air freight rate per kilogram for shipments from China varies according to different weight categories. There are five principal pricing tiers: shipments over 45KG, 100KG, 300KG, 500KG, and 1000KG.
In instances where a specific weight category doesn't correspond to a set rate, the applicable freight charges are calculated based on the TACT (The Air Cargo Tariff) rates.
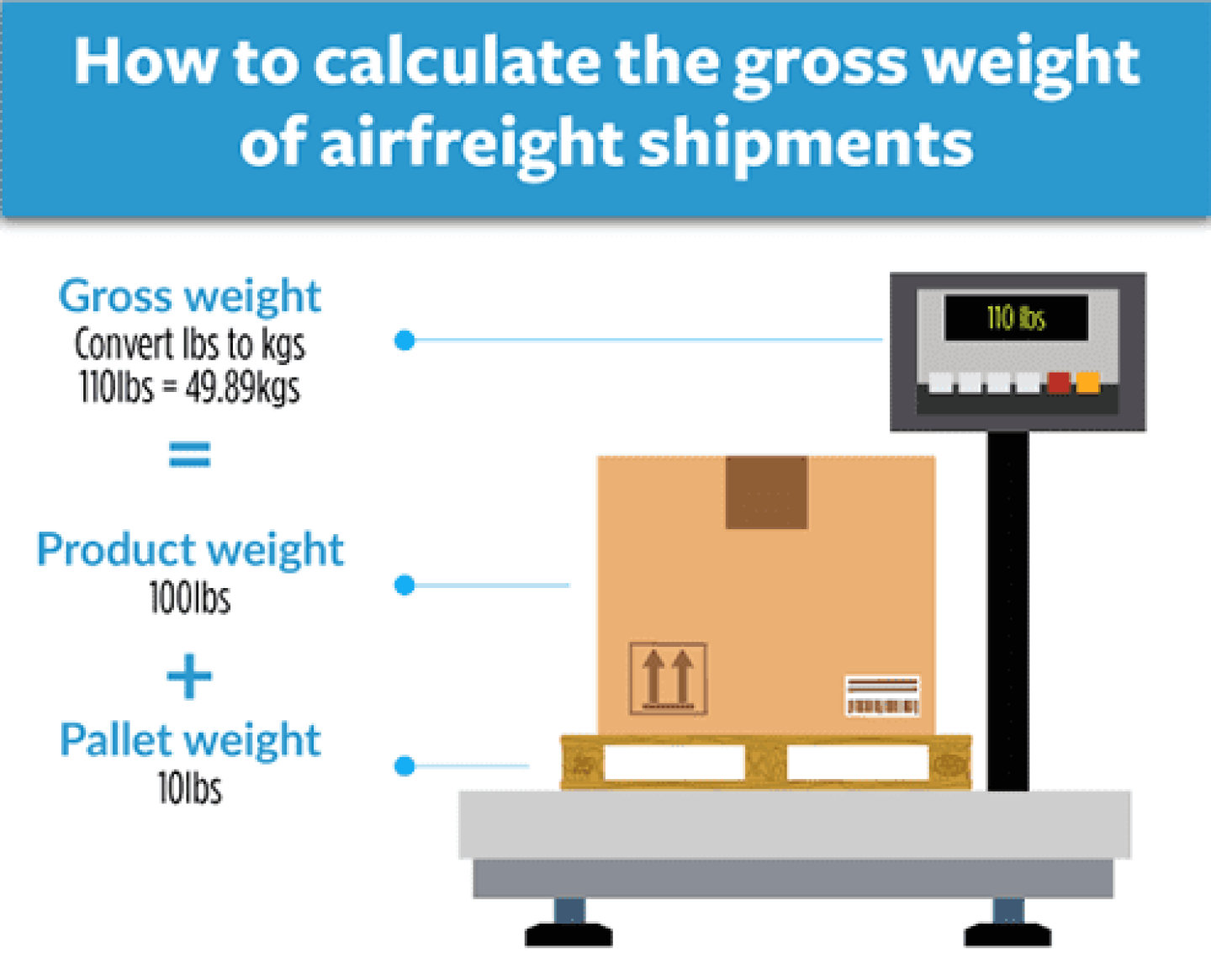
An essential factor in determining the final cost is the chargeable weight, which is derived from either the volumetric weight or the gross weight of the goods.
If the volumetric weight exceeds the gross weight, the chargeable weight will be based on the volumetric weight. Conversely, if the gross weight is higher, the chargeable weight will be based on the actual gross weight.
Chargeable Weight in Air Freight for Gross Weight and Volume Weight Cargo
Understanding Air Freight Chargeable Weight
Air freight chargeable weight refers to the weight used for calculating the shipping cost of a cargo. This could be based on either the gross weight or the volumetric (volume) weight of the shipment. Common units for measuring these weights are grams and kilograms.
High-Density Cargo (Heavy Cargo)
In China: High-density cargo is defined as cargo having a weight exceeding 1 kg per 6,000 cubic centimeters, or 166.67 kg per cubic meter (1 CBM).
Internationally: High-density cargo is identified as cargo that weighs more than 1 kg per 166 cubic inches, or 1 pound per 166 cubic inches.
For high-density cargo, the chargeable weight is determined by the actual gross weight of the shipment.
Billing and Weight Units
The gross weight of the goods is measured in kilograms. The minimum unit of billable weight is either 0.5 kilograms or 1 kilogram, as set by each airline.
- When the smallest billing unit is 0.5 kg, weights less than 0.5 kg are rounded up to 0.5 kg. Weights greater than 0.5 kg but less than 1 kg are rounded up to 1 kg.
- When the smallest billing unit is 1 kg, all weights less than 1 kg are rounded up to 1 kg.
This ensures that the shipment charges are standardized for various weight ranges and comply with the airline's billing policies.
Volume Weight Calculator for Air Freight (Light Cargo)
Definitions:
- A: Actual gross weight
- B: Volume weight
When A exceeds B, the cargo is classified as high-density; conversely, if A is less than B, the cargo is considered light.
Criteria:
- In China: Light cargo refers to items weighing less than 1 kg per 6,000 cubic centimeters or under 166.67 kg per cubic meter (CBM).
- Internationally: Light cargo is defined as those weighing less than 1 kg per 366 cubic inches or less than 1 pound per 167 cubic inches.
Chargeable Weight Calculation:
For light cargo, the dimensional weight is regarded as the chargeable weight. The calculation method is as follows:
-
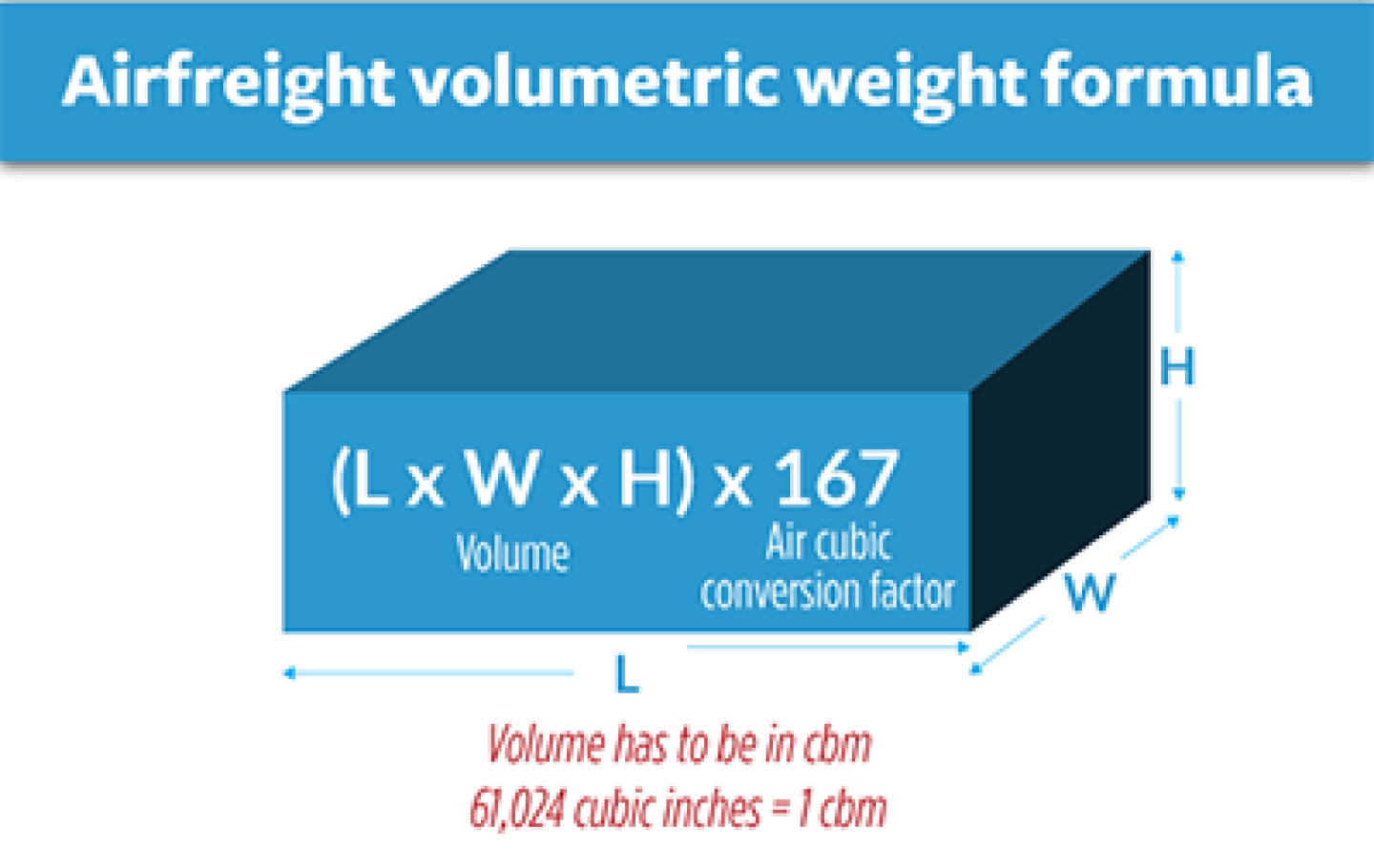
Measurement: Regardless of the geometric shape of the goods, measure the length, width, and height in centimeters (cm), meters (m), or inches (in).
-
Formulas:
- Volume weight (kg) = (\frac{length (cm) \times width (cm) \times height (cm)}{6000})
- Volume weight (kg) = Cargo volume (in cubic meters) (\times 167) kg
- Volume weight (kg) = (\frac{Cargo volume (in cubic inches)}{366})
- Volume weight (lbs) = (\frac{Cargo volume (in cubic inches)}{166})
This calculation ensures accurate billing for air freight based on the dimensional weight of the cargo.
